[ccfic]
In 2013, the United Nations (UN) designated 31st October as World Cities Day to promote global sustainable urban development with the aim to raise awareness about global urbanisation and push for cooperation in addressing specific challenges that affect cities. This is closely linked to the UN’s Sustainable Development Goal 11 – ‘Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable’ (1).
Importance of World Cities Day and sustainable cities
World Cities Day focuses attention on the number of people living in urban areas and the inequalities they face. Predictions suggest that by 2050, 68% of the world’s population will live in urban areas due to both a growing population and a gradual shift of people to these areas (2) . As urbanisation accelerates, cities are experiencing the effects of climate change including rising temperatures, increasing flood risk, and poor air quality. The high concentration of people and infrastructure in cities intensifies the impact of climate change and highlights the need for a transition to sustainable thinking. Sustainable urban development is key to addressing climate inequality and ensuring cities are liveable for future generations.
Sustainable cites can be analysed using four key dimensions (3); environmentally sustainable, resilient, inclusive and competitive.
- Sustainable urban development helps combat climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions through efficient energy use, green infrastructure, and sustainable transportation options.
- Resilience against natural disasters and adapting to changing environmental conditions, creates environments that are not only suitable for current residents but also viable for future generations.
- Prioritising inclusivity and social equity, ensures that all residents have access to essential services, green spaces, and clean air, which contributes to improved public health and quality of life.
- Competitive communities ensures that cities can stay productive with jobs generated for members of the community.
Investing in sustainable urban environments is crucial for creating a balanced relationship between humans and the natural world, ensuring that urban areas can thrive while protecting the planet. Geospatial data and smart city technology can be used in the drive towards sustainable urban development.
Geospatial data for smart cities
Smart cities can be described as urban areas where technology and data are used to improve urban living and enhance sustainability and efficiency (4). The concept of smart cities focusses on integrating information and data with city services to manage resources effectively, reducing environmental impact and thereby promoting sustainable living. Geospatial data is a foundational element for smart cities and is a valuable resource for sustainable urban development.
In urban environments, data and technology can be used to support sustainable urban areas by providing data-driven solutions. These solutions are a key aspect of smart cities and include tracking environmental change, sustainable infrastructure, enhancing public transport, and optimising land use.
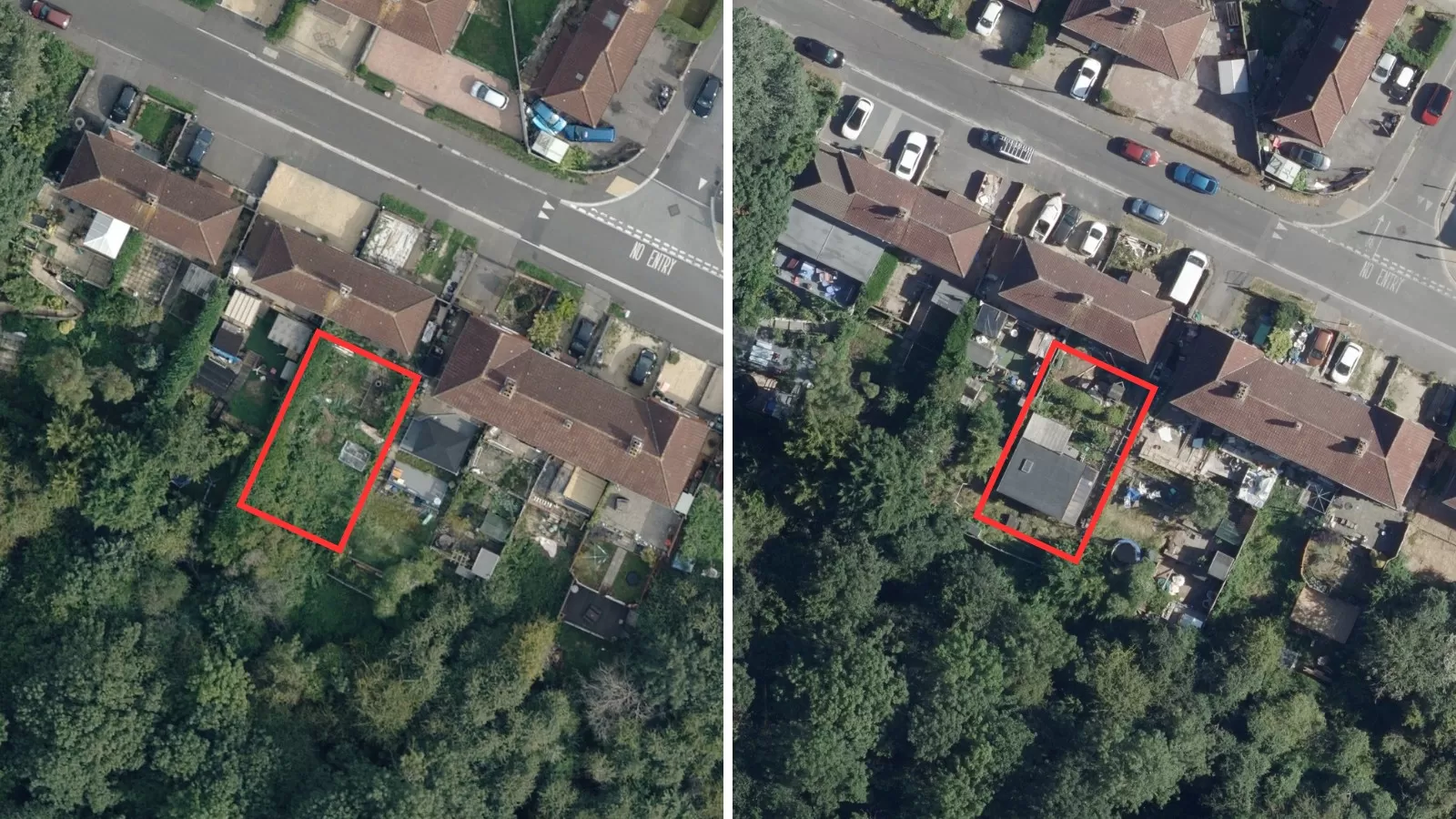
Geospatial datasets such as 3D models and aerial photography can be used to understand the distribution of green infrastructure in a city. This includes renewable energy sources such as solar panels, green cover such as green roofs, and maximising energy distribution using smart grids. 3D models have become the key to unlocking the value of smart cities and provide an alternative to traditional 2D GIS solutions.
MetroVista™: a game changer for urban planning
One product that harnesses the power of geospatial data for sustainable urban development is Bluesky’s MetroVista™ (5). This innovative data solution combines high-resolution aerial imagery with oblique imagery and LiDAR data to create detailed 3D mesh models of urban environments. Using cutting-edge airborne sensor technology, the MetroVista™ datasets are acquired simultaneously facilitating the creation of truly co-registered products that can be used independently or combined to generate vibrant and interactive 3D digital cityscapes.
MetroVista™ offers a foundation to make smart decisions in a rapidly changing urban environment. There are a diverse range of applications for 3D mesh models including urban planning, architecture, public engagement, defence and security, utilities, insurance and modelling and visualisations.
Intelligent 3D mapping provides a real-world context to assist with planning. The existing urban environment and buildings can be viewed by age, size, cost and postcode. Proposed developments and potential buildings can be virtually inserted to understand visual impacts and provide accurate measurements – all from a desktop, saving time and resources. Using 3D models can aid with cost-saving utility management, for example by plotting masts with real-world precision to analyse the most efficient network taking line-of-sight into consideration.
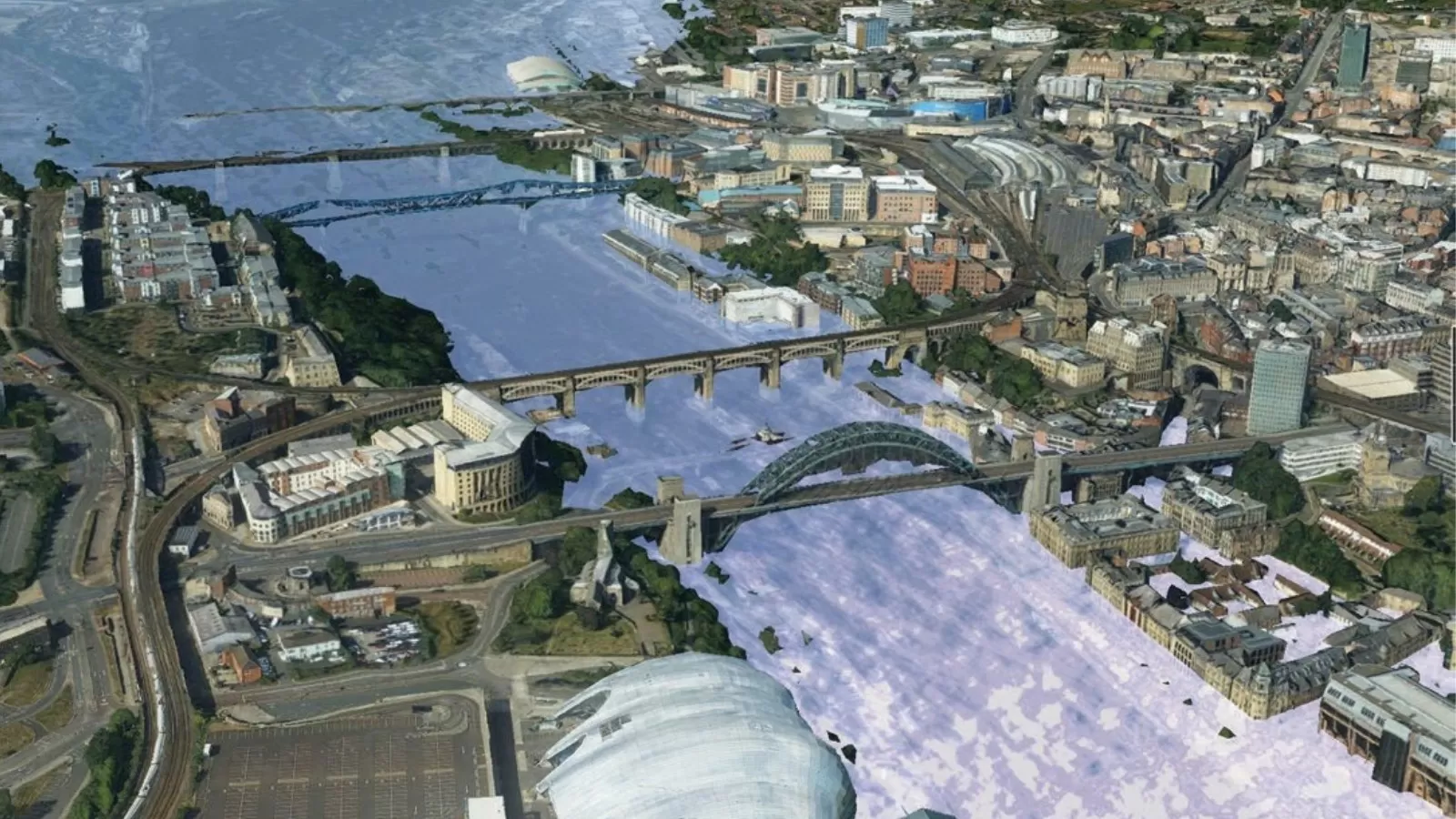
Scenario modelling is possible with MetroVista™ to understand defence and security risks, and to support environmental modelling. The complexity of cities makes it hard to manage security. Analysing potential threat domes and understanding line-of-sight can be an invaluable tool when planning for public safety. Fluid dynamic modelling for flood management and pollution modelling based on different scenarios offers an understanding of the potential impact of specific climate events. Once we understand this, we can start to plan how to mitigate against them.
Additionally, the combination of oblique imagery and 3D mesh models can benefit the emergency services with future planning or live monitoring during any given event. For example, MetroVista™ shows a level of detail of individual buildings, including the number of windows and location of doors. With MetroVista™ integrated into a GIS system, emergency service operators can conduct desktop analysis before and during an event as an aid.
The accuracy and detail included in MetroVista™ means the data can be used for visualisations making it, not only an invaluable planning tool, but also an invaluable public engagement tool. Planners, local authorities, policy makers, the utility sector and more can engage those that live and work in our cities using tools like MetroVista™ which offer an effective vehicle to clearly communicate proposed change.
The wide range of applications for MetroVista™ can help organisations create sustainable cities that are environmentally sustainable, resilient, inclusive and competitive. The ability to use a combination of datasets in one environment to create highly accurate, and detailed 3D cityscapes opens up multiple opportunities for digital planning and sustainable urban development, both now and in the future.
Conclusion
In the age of conflicting pressures of urban expansion and environmental impact, it has never been so important to have the ability to visualise, analyse and manipulate a digital version of our physical surroundings. World Cities Day promotes global cooperation in creating sustainable urban environments to address inequalities, particularly related to climate change. Using geospatial data tools such as Bluesky’s MetroVista™ provides unmatched levels of detail and accuracy, invaluable for mapping and monitoring our 3D environment. Mesh models provide spatially and geometrically accurate data that can be used for analysis making them a powerful tool for all urban practitioners.